Introduction of HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a lentivirus (a member of the retrovirus family) that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
A condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive.
HIV was first observed in 1981 in new York .
USA ,In 1983-retrovirus was isolated by luc Montagnier and colleagues from Pasteur institute ,paris
It was first labeled as LAV(lamphadenopathy associated virus ) and HTLV-3 (human immunodeficiency virus)by the International committee on virus Nomenclature
Types of HIV infection:-
Two types of HIV infect humans:
- HIV-1
- HIV-2.
HIV-1 is more virulent, is more easily transmitted and is the cause of the vast majority of HIV infections globally.
The pandemic strain of HIV-1 is closely related to a virus found in the chimpanzees of the subspecies Pan troglodytes troglodytes,.
HIV-2 is less transmittable and is largely confined to West Africa, along with its closest relative to SIV(semen immunodeficiency virus) of the sooty mangabey (Cercocebus atys atys), an Old World monkey Infection with HIV occurs by the transfer of blood, semen, vaginal fluid, pre-ejaculate, or breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected immune cells.
The four major routes of transmission are
1. unsafe sex,
2. contaminated needles,
3. breast milk,
4. Transmission from an infected mother to her baby at birth (perinatal transmission).
Screening of blood products for HIV has largely eliminated transmission through blood transfusions or infected blood products in the developed world.
HIV infection in humans is considered pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO). Nevertheless, complacency about HIV may play a key role in HIV risk.
From its discovery in 1981 to 2006, AIDS killed more than 25 million people. HIV infects about 0.6% of the world’s population
. In 2009, AIDS claimed an estimated 1.8 million lives, down from a global peak of 2.1 million in 2004.] Approximately 260,000 children died of AIDS in 2009 A disproportionate number of AIDS deaths occur in Sub-Saharan Africa, retarding economic growth and exacerbating the burden of poverty.
An estimated 22.5 million people (68% of the global total) live with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa, which is also home to 90% of the world’s 16.6 million children orphaned by HIV Treatment with antiretroviral drugs reduces both the mortality and the morbidity of HIV infection.
Although antiretroviral medication is still not universally available, expansion of antiretroviral therapy programs since 2004 has helped to turn the tide of AIDS deaths and new infections in many parts of the world.
Intensified awareness and preventive measures, as well as the natural course of the epidemic, have also played a role. Nevertheless, an estimated 2.6 million people were newly infected in 2009.
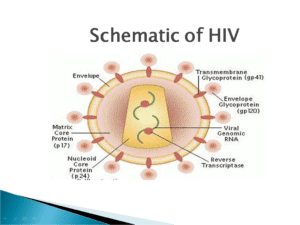
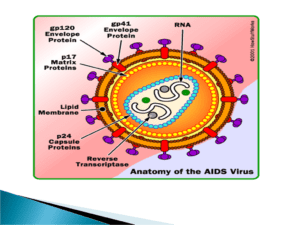
Structural character
- Hiv is spherical shape , enveloped RNA virus
- Size – 90-120nm in diemeter
- Nucleo capsid –has outer icosahedral shell and inner cone shaped
- Genome– consist of two identical single –stranded (positive sense)RNA copies and reverse transcriptase enzyme which is a character of retro virus
- Envelope– is lipoprotein in nature , having matrix protein and host cell derived lipid bilayer envelope from which glycol protein peplomers project
Hiv contain different structural gene & non structural gene such as Envelope Ags(antigen surface) - Spike- gp120(Glycoprotein)
- Trans membrane pedicle Ag- gp41
- Gag Ag- core and shell Ag
- Shell- nucleocapsid Ag-gp18
- Core-Major Ag-P24 (polymerase)
- Other-Ag p55 ,p15
Pol Ag – p31,p51,p65
Non structural gene
- Tat (trans activating gene) –enhances expression of viral gene
- Nef (negative factor gene)- Down regulates viral replication
- Vif (viral infectivity factor gene) – influence infectivity of viral particles
- Vpu(in HIV-1 only) and vpx (only in HIV-11) enhance maturation and release of progeny virus
- Vpr- stimulating, promoter region of virus
- LTR(long terminal repeat sequence) gives promoter ,enhancer and integration signals.
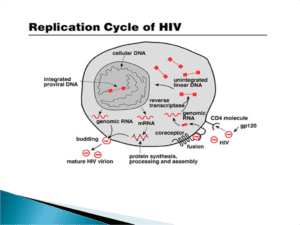
HIV infects vital cells in the human immune system such as
1. helper T cells (specifically CD4+ T cells),
2. macrophages,
3. and dendritic cells.
HIV infection leads to low levels of CD4+ T cells through three main mechanisms:
A. Direct viral killing of infected cells;
B. Increased rates of apoptosis in infected cells;
C. killing of infected CD4+ T cells by CD8 cytotoxic lymphocytes that recognize infected cells.
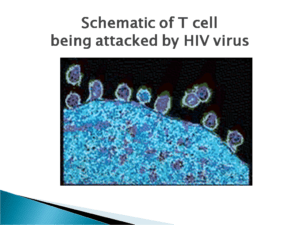
When CD4+ T cell numbers decline below a critical level, cell-mediated immunity is lost, and the body becomes progressively more
Resistance of HIV
• HIV is delicate virus, thermo labile- (destroyed in 10 min at 500c and in seconds at 1000c) and survive at room temperature for seven days
• HIV disinfectant such as
70% ethyl alcohol
0.5% lysol
o.1% formalin
2% glutaraldehyde
0.3% hydrogen peroxide
0.2% hypochlorite
10% household bleach
Clinical Stages of HIV Infection
• Primary – Acute
• Asymptomatic
• Symptomatic
• AIDS
Primary – Acute Stage
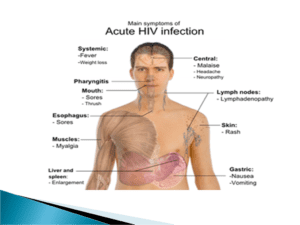
- During this stage most people are asymptomatic. Some people may have symptoms of a viral infection that usually lasts a few days.
- These symptoms may include: fever, cough, runny eyes or nose, swollen lymph glands, rash and fatigue . These symptoms may appear 2 – 4 weeks after exposure to the HIV virus.
Asymptomatic Stage
- This stage is a time of viral replication. People have no symptoms but are infectious. Risky behavior such as unprotected sex or IV drug use can transmit the HIV virus.
- This stage can last as long as 10-12 years or as short as several months.
AIDS Related Complex Stage
- Symptoms associated with this stage include:
- night sweats, chills, fever, diarrhea or pneumonia and the appearance of opportunistic infections.
At this time CD4 counts are usually 300-500. (normal
CD4 count is 800 – 1000)
During this time many people can perform their normal activities and continue to work.
AIDS Stage
- When CD4 cell count falls below 200 and a person has been diagnosed with AIDS defining illnesses – the diagnosis of AIDS is made.
- Some of the AIDS defining illnesses are:
- Kaposi’s sarcoma
- Pneumocystis pneumonia
- Toxoplasmosis
- Esophageal Candidacies
- Thrush
- Invasive Candida vaginitis – in women
• Bacterial - Strep pneumonia
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB)
- Mycobacterium avium(MAI)
Viral
- Herpes
- Varicella Zoster
- CMV / EBV
- Influenza
Parasites
- Pneumocystis carinii
- Toxoplasmosis
- Cryptosporidum
Fungus
- Candida
- Aspergillus
- Cryptococcus
MALIGNANCIES IN AIDS AIDS defining
- Kaposi’s sarcoma
Primary CNS(brain lymphoma
High grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Invasive carcinoma of the cervix
Anorectal squamous carcinoma
Hodgkin’s disease
Infection in Human
HIV and AIDS Infection in Women
- Third leading cause of death
- women between the ages of 25-44
- leading cause of death of African American women of this age group
- Usual exposure is unprotected sex
- HIV and AIDS increasing more rapidly in women than any other group of people.
HIV / AIDS Infection in Children
- Florida – 2nd highest rate in U.S.
- > 96% of cases – transmission from mother
- Diagnosis made by DNA testing
- Treatment of HIV positive mothers – to decrease transmission
- In children it is especially important to maintain/reconstitute their immune systems
- Children have higher level of virus initially
- There is more rapid disease progression in children
- Some signs/symptoms of HIV in children include unexplained fevers, failure to thrive, swollen lymph glands, fatigue.
Mode of Transmission:
| TYPES OF EXPOSURE
INFECTION |
APPROXIMATE CHANCE OF INFECTION |
| Sexual intercourse : (anal, vaginal, oral)
|
0.1-1.0% |
| Blood &blood product
Factor 7 blood transfusion |
ñ90 |
| Tissue and organ donation :semen ,cornea , bone marrow , kidney | 50-90% |
| Injection & injuries :share needle injection by unsterile syringe & needle | 0.5-1.0% |
| Mother to baby
trans-placental At birth After birth Breast milk |
30% |
Method of Test:-
HIV TESTING
- Antibody Detection (ELISA / WB)
- Antigen Detection (P24)
- RNA and DNA Detection(Viral load/ PCR)
Procedure of HIV Test by ELISA method
Set up the micro titration wells in the frame and label one well as blank and two wells each as positive and negative control
↓
100 µl sample dilution is taken in antigen coated micro titration well
↓
Added 50 µl sample in the wells
↓
Cover the wells with adhesive slip
↓
Incubate at RT for 30 min(250-300)
↓
Aspirate and dispose the sample along with microtip s into a container containing 0.5% sodium hypo chloride solution
↓
Wash the wells 5 times by wash buffer
↓
100 µl HRP conjugate is added
↓
Incubate at RT for 30 min
↓
Wash the wells 5 times by wash buffer
↓
100 µl of working TMB substrate in the wells
↓
Incubate at RT for 30 min(250-300)
↓
Stop the reaction by adding 100 µl of the stop solution
Observation:-
Blue colour is observed which matched with the colour of positive control.
Antigen Detection (P24)
10 µl of serum or plasma /20 µl whole blood is taken in to the sample well(s) using micropipette
⇓
Add 4 drop of diluents in to sample well.
⇓
Left for 5-20 min after adding diluents.
⇓
The purple colour develops across the result center of the device.
Result :-
- one line shows negative result
- Two line shows positive result
- Three line shows positive result(HIV1/2)
Normally I do not read article on blogs however I would like to say that this writeup very forced me to try and do so Your writing style has been amazed me Thanks quite great post
It was great seeing how much work you put into it. The picture is nice, and your writing style is stylish, but you seem to be worrying that you should be presenting the next article. I’ll almost certainly be back to read more of your work if you take care of this hike.
I do agree with all the ideas you have introduced on your post They are very convincing and will definitely work Still the posts are very short for newbies May just you please prolong them a little from subsequent time Thank you for the post
Hi i think that i saw you visited my web site thus i came to Return the favore I am attempting to find things to improve my web siteI suppose its ok to use some of your ideas
Hi Neat post There is a problem along with your website in internet explorer would test this IE still is the market chief and a good section of other folks will pass over your magnificent writing due to this problem
I enthusiastically began reading this awesome website a couple days ago, they have really good content for their followers. The site owner has a talent for captivating readers. I’m delighted and hope they maintain their excellent efforts.
Somebody essentially lend a hand to make significantly articles Id state That is the very first time I frequented your website page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to make this actual submit amazing Wonderful task
obviously like your website but you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand Ill certainly come back again
As a Newbie, I am always searching online for articles that can aid me. Thank you