Bacterial Endotoxin Test in Injectable Plant: Principles, Methods, and Applications
Bacterial Endotoxin Test:-
Bacterial endotoxins, also known as lipopolysaccharides (LPS), are complex molecules found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. They are potent pyrogenic substances that can cause fever, inflammation, and other adverse effects in humans and animals. Injectable pharmaceuticals, such as parenteral drugs, vaccines, and medical devices, are particularly susceptible to endotoxin contamination, as they are intended for direct administration into the bloodstream or other sterile body compartments. Therefore, the bacterial endotoxin test (BET) is a critical quality control test performed in injectable plant facilities to ensure the safety and efficacy of injectable pharmaceutical products.
This article provides an in-depth overview of the principles, methods, and applications of the bacterial endotoxin test in an injectable plant setting, including the regulatory requirements, sample preparation, test methods, and interpretation of results.
Regulatory Requirements for Bacterial Endotoxin Test in Injectable Plant
The bacterial endotoxin test is a mandatory test required by regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other regulatory authorities, for injectable pharmaceutical products. It is performed as part of the release testing and stability testing of injectable drugs to ensure compliance with regulatory standards for endotoxin limits.
The regulatory requirements for the bacterial endotoxin test in an injectable plant may vary depending on the specific product, country, and regulatory agency. In general, the regulatory requirements for the bacterial endotoxin test include:
Endotoxin limits: Regulatory agencies specify the maximum allowable endotoxin limits for different types of injectable pharmaceutical products, such as intravenous (IV) drugs, intramuscular (IM) drugs, and vaccines. These limits are based on the route of administration, intended patient population, and therapeutic indication, and are established to ensure patient safety and product quality.
Test methods: Regulatory agencies provide guidance on the test methods to be used for the bacterial endotoxin test, which are based on the compendial methods, such as the Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) assay or the recombinant Factor C (rFC) assay. These methods are validated, standardized, and widely accepted for the detection and quantification of endotoxins in injectable pharmaceuticals.
Sample preparation: Regulatory agencies provide guidance on the sample preparation procedures for the bacterial endotoxin test, which typically involve dilution or extraction of the injectable product to remove potential interfering substances and to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Validation: Regulatory agencies require the validation of the bacterial endotoxin test method used in the injectable plant, which involves demonstrating the reliability, accuracy, and reproducibility of the method for the specific product and sample matrix.
Documentation: Regulatory agencies require documentation of the bacterial endotoxin test results, including test data, calculations, and interpretations, as part of the product release and stability testing records. These records should be maintained in accordance with regulatory requirements and should be available for inspection by regulatory agencies during audits or inspections.
Methods for Bacterial Endotoxin Test in Injectable Plant
The bacterial endotoxin test is based on the principle of the interaction between endotoxins and the Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) or recombinant Factor C (rFC) in the presence of a chromogenic or turbidimetric substrate. The LAL assay is the most commonly used method for the bacterial endotoxin test in injectable plant facilities, although the rFC assay is gaining popularity due to its advantages in terms of specificity, stability, and potential for automation.
You may also read depyrogenation tunnel is a pharmaceutical manufacturing
Definition
-
Endotoxin: Lipo-polysaccharide entity of gram-negative bacteria cell wall that causes fever.
-
Endotoxin Limit (EL): The maximum amount of Endotoxin allowed in a drug which is allowed to be administered in human body. It is expressed in EU or IU.
-
Endotoxin unit: Measurement of the biological activity of an Endotoxin preparation. One International unit (IU) of Endotoxin is equal to one Endotoxin unit (EU).
-
Maximum Valid Dilution (MVD): The maximum valid dilution is the dilutions up to which a drug can be diluted and still detect the Endotoxin content present in the sample. MVD can be calculated by the formula given below:

-
Control Standard Endotoxin (CSE): Lyophilized vial containing secondary Endotoxin standards supplied by the manufacturer.
Two basic functions of CSE are:
1) To confirm LAL test validity by recovery of PPC.
2) Lysate validation to confirm the sensitivity of Lysate at the user end.
-
LAL Reagent Water (LRW): Highly purified water having very less concentration of Endotoxin which does not interfere with the LAL testing procedure.
-
Labeled sensitivity of the Lysate (λ): Minimum concentration of Endotoxin required to cause the lysate to clot under standard conditions is the sensitivity of the lysate which is labeled on the lysate vial.
-
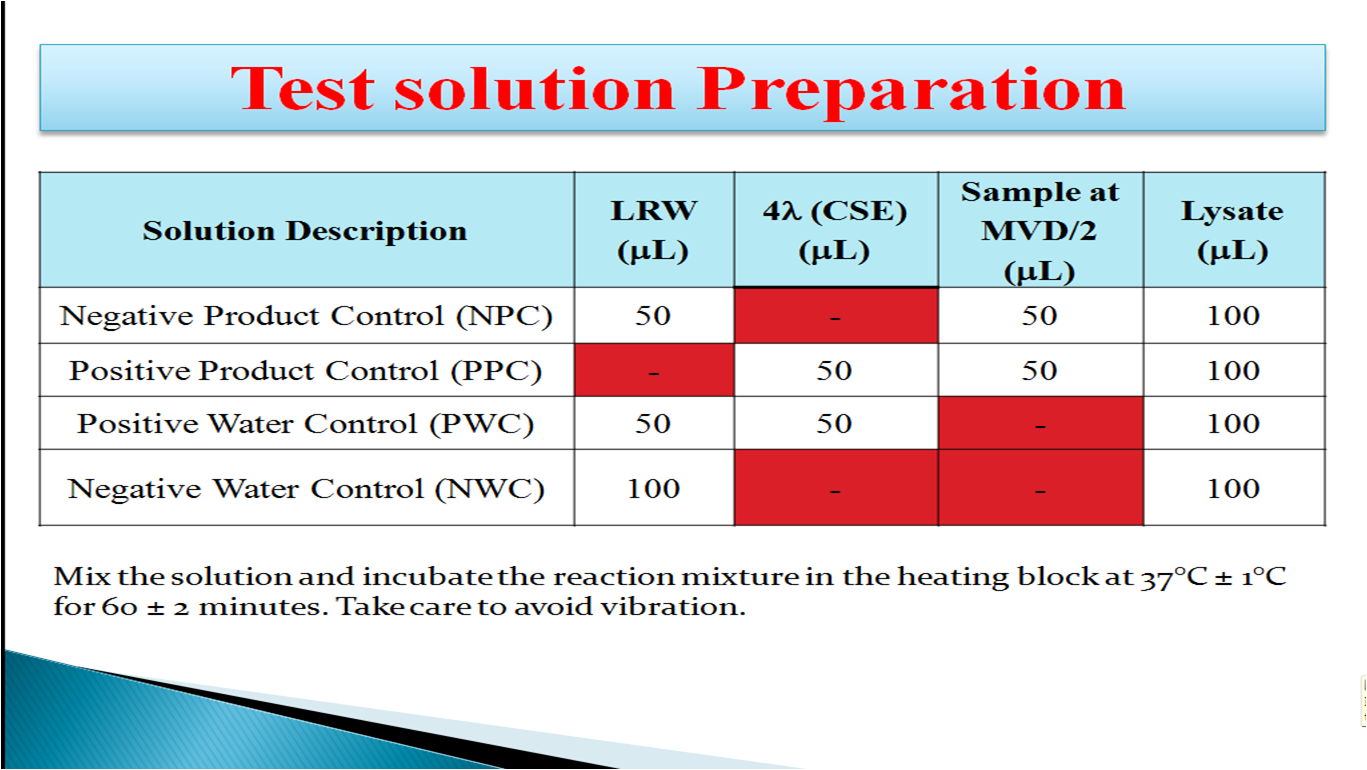
Positive Product Control (PPC): This is a sample spiked with Endotoxin that gives a positive result with firm gel. The positive product control must be tested with each sample to ensure that a result is valid and free from interference of product.
-
Positive Water Control (PWC): This is LAL reagent water spiked with Endotoxin that gives a positive result with firm gel. The positive water control must be tested with each test to ensure that the LAL reagent water does not interfere with the gel formation.
-
Negative Water Control (NWC): This is the LAL reagent water and Limulus amoebocyte lysate reagent mixture used as a control to ensure that reagent and accessories used are free of Endotoxin when it gives negative result with no gel formation.
-
Maximum Valid Dilution

-
How to Prepare Sample Dilution

-
Maximum Valid Concentration:

-
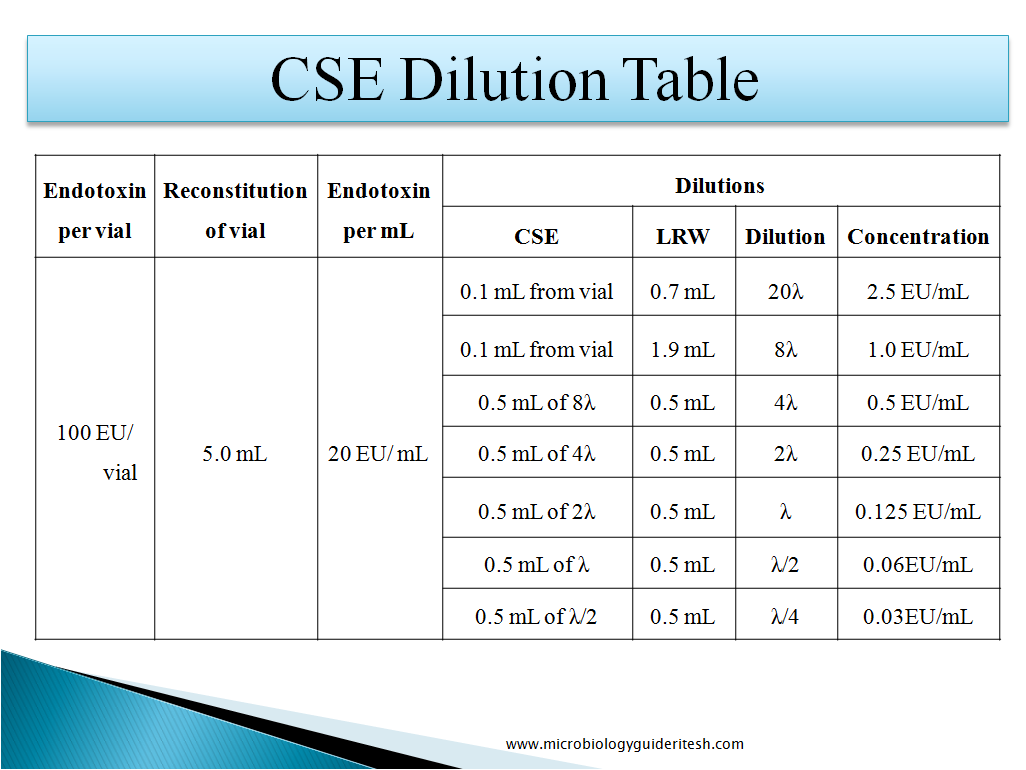
How to Prepare CSE Dilution:-

- How to Prepare Test Solution:
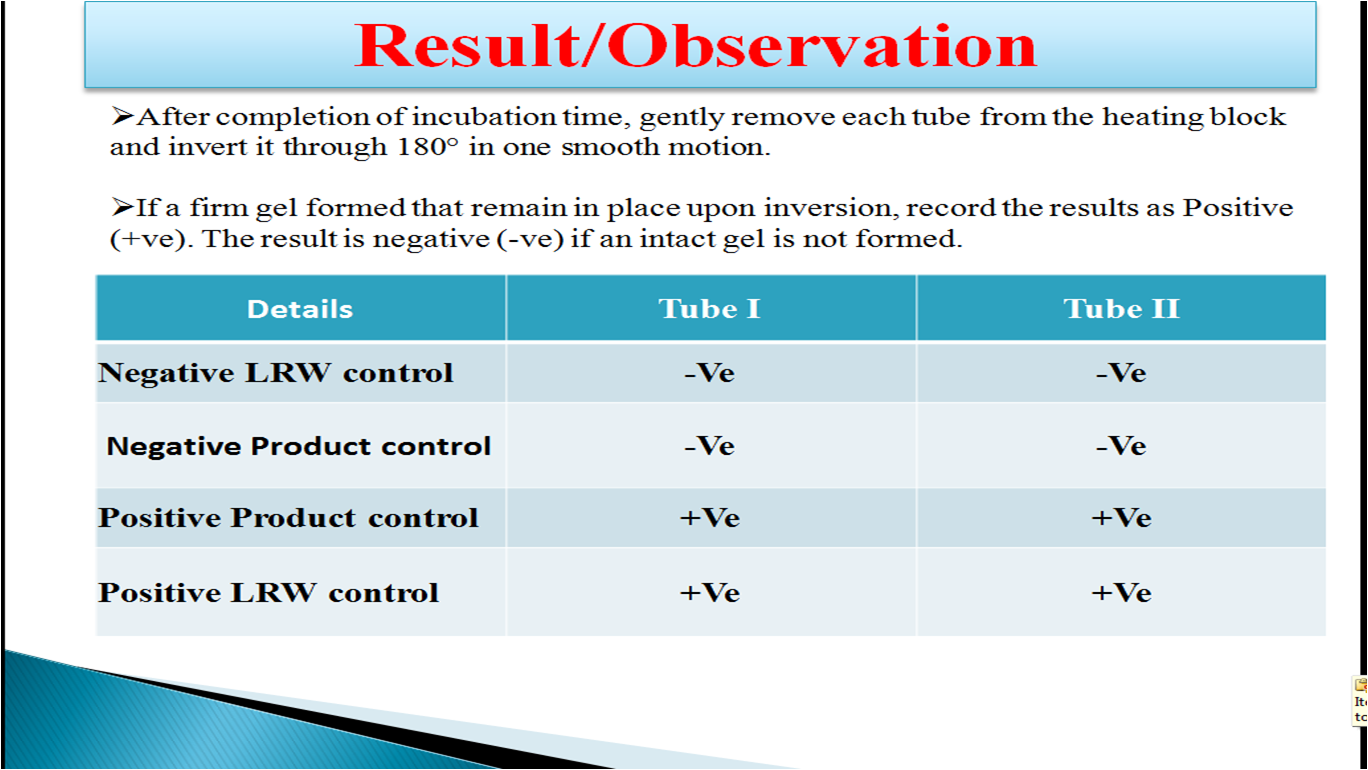
Interpretation of Result
Pingback:-



I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this increase.
The crux of your writing while sounding agreeable originally, did not sit very well with me personally after some time. Someplace within the paragraphs you were able to make me a believer but only for a very short while. I still have a problem with your leaps in logic and one would do well to help fill in all those gaps. In the event that you can accomplish that, I will certainly end up being amazed.
Aw, this was a very nice post. In idea I wish to put in writing like this moreover – taking time and precise effort to make a very good article… however what can I say… I procrastinate alot and not at all seem to get one thing done.